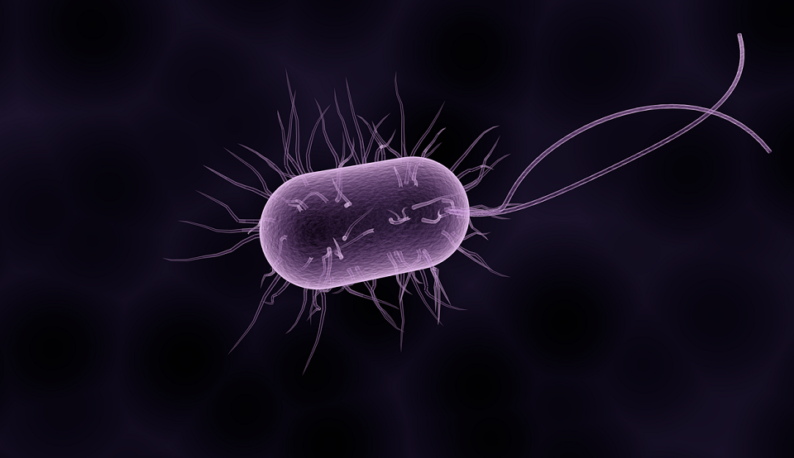
In addition to posing obvious public health risks, some bacteria may also affect different industries on several levels. For instance, water filtration and desalination systems are affected by a process known as biofouling, which consists in the attachment and accumulation of bacteria to the covering layer of these devices’ surfaces.
One possible solution to mitigate this problem, which reduces the life-span of the membranes and inflicts health and economic damage, is to use antibacterial coatings. This is what has been studied by a team of researchers from the Federal University of Ceará, with an emphasis on cellulose nanocrystal coatings (CNCs).
In an article published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering, researchers describe how surfaces coated with these nanocrystals were able to render inactive up to 90% of the Escherichia coli (or E. coli) cells, which can be harmful to the human gastrointestinal tract, depending on the bacterial strain, if it is present in food, for example.
With the research findings, a gap in the knowledge about cellulose nanocrystals has been closed: the toxicity mechanisms of the CNCs for microorganisms such as E. coli, since previous studies had already demonstrated their antibacterial potential, but the reasons were not yet clear.
“The proposed toxicity mechanism for the material is physical contact with the microorganism”, Victor Teixeira Noronha, a Ph.D student of the Natural Resources Biotechnology Program at UFC and one of the authors of the study, explains. “Whereas most approaches are based on the use of chemical compounds to interrupt biochemical processes in microorganisms, cellulose nanocrystals work by inflicting physical stress upon them.”
This means that cellulose nanocrystal coatings (CNCs) inactivate the bacteria because of their needle-like structures that puncture the microorganisms’ cell membrane. It is due to this action that the bacteria lose their lipid layers, which function as barriers and protect them from damage.
In order to reach these results, the E. coli were placed in contact with a surface composed of CNC for three hours, then the bacterial cells attached to the area were counted. Additionally, filters with no CNC were used as control. When comparing the materials, a difference of 90% in the contamination rate was noticed, which also depends on the concentration of nanocrystals in the coating.
CELLULOSE
With the increasing demand for nanomaterials with antimicrobial activity, CNCs take the spotlight not only for their effectiveness but also for the practicality offered by the raw material they use, which is abundant in nature. Cellulose can be found in plant cells, including their leaves, fibers and wood, thus facilitating the process of nanocrystal production.
Other alternatives for antibacterial coatings had already been tested, such as polymers made from materials called zwitterion, ammonia compounds, and nanomaterials such as graphene oxide and silver nanoparticles, but each of them has its disadvantages, either concerning the use itself or the risks posed to the environment.
Considering the success of the studies about cellulose nanocrystals and their ability to reduce the biofouling process, researchers are now evaluating how to make these materials’ mechanism of action even more efficient.
“The incorporation of other materials in the nanocrystals is also being studied, with the aim of further improving their antibacterial properties. The intention for future analyses is to also introduce bacteria that are more commonly found in these water filtration and desalination systems, and not just the sampled bacteria”, Victor estimates.
TEAM
The study was carried out by the UFC association with the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP, in the Portuguese acronym) and the University of Florida (USA). Also participating in the research are the Professors Amauri Jardim de Paula and Antonio Gomes de Souza Filho, from the UFC Physics Department; Professor Camila Rezende and researcher Camilla Camargos, from the Institute of Chemistry at UNICAMP; and Professor Andreia Faria and researcher Jennifer Jackson, from the Environmental Engineering Sciences Department at the University of Florida.
The full article published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering is available here.
Source: Victor Teixeira Noronha, from the Graduate Program in Natural Resources Biotechnology – email address: victor.noronha@fisica.ufc.br
Translation: Isabelly Maia – Research Assistant at UFC’s Translation Laboratory (LETRARE/PROINTER)